A Mean Calculator is a fast and reliable tool designed to help you calculate the average of any set of numbers in seconds. Whether you are working on homework, analyzing business data, reviewing exam scores, or managing financial records, this Mean Calculator allows you to enter your values and instantly get accurate results without manual calculation errors.
Instead of adding numbers one by one and dividing them yourself, the calculator performs the full process automatically and shows you the correct arithmetic mean with precision.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is the Mean in Mathematics?
In mathematics and statistics, the mean is commonly referred to as the average. More specifically, it is called the arithmetic mean, and it represents the central value of a group of numbers. To calculate the mean manually, you add all the numbers together and then divide that total by how many numbers there are.
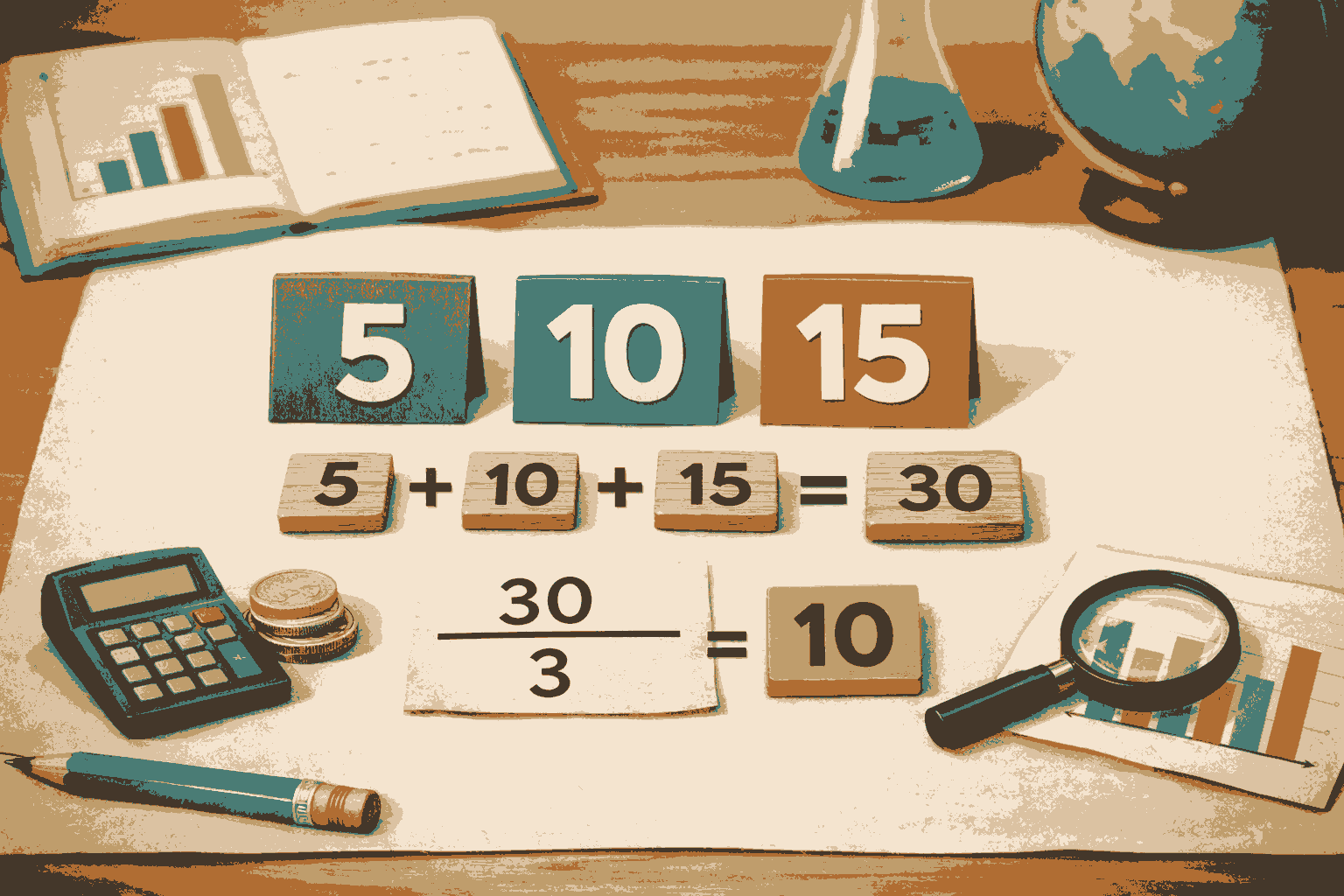
For example, if you have the numbers 5, 10, and 15:
5 + 10 + 15 = 30
There are 3 numbers
30 ÷ 3 = 10
The mean is 10.
The purpose of the mean is to summarize a dataset into a single representative value. Instead of looking at every individual number, you can understand the overall trend or level of the data through its average. This makes it one of the most widely used measures in education, science, economics, and everyday life.
How This Mean Calculator Works
This Mean Calculator follows the exact mathematical formula used in textbooks and statistical analysis. When you enter a list of numbers separated by commas, spaces, or line breaks, the tool performs three core steps.
- First, it identifies and validates each number in the list.
- Second, it calculates the total sum of all valid numbers.
- Third, it divides the sum by the total count of numbers entered.
The result shown is the arithmetic mean of the dataset.
Because the calculator processes the values automatically, it eliminates common mistakes such as skipping a number, miscalculating the sum, or dividing incorrectly. It also works with positive numbers, negative numbers, decimals, and large datasets, making it useful for both basic math and advanced data analysis.
Mean Formula Explained
The formula for calculating the mean is simple:
Mean = (Sum of all values) ÷ (Number of values)
In mathematical notation, this is written as:
Mean = (x₁ + x₂ + x₃ + … + xₙ) ÷ n
Where x represents each individual value and n represents the total number of values.
This formula ensures that every value contributes equally to the final result. Unlike the median, which depends on order, or the mode, which depends on frequency, the mean uses every number in the dataset.
For example, if you have four test scores: 70, 80, 90, and 100:
70 + 80 + 90 + 100 = 340
340 ÷ 4 = 85
The mean score is 85.
This formula is the foundation of statistical analysis and is applied in nearly every field that relies on numerical data.
Why Use an Online Mean Calculator?
While calculating averages by hand is straightforward for small datasets, it becomes time-consuming and error-prone when dealing with many numbers. An online Mean Calculator offers significant advantages.
- It provides instant results without manual arithmetic.
- It accurately handles decimal and negative values.
- It saves time for students and professionals.
- It reduces the risk of calculation errors.
- It works efficiently even with large datasets.
Students often use it to double-check homework answers. Teachers use it to compute class averages. Business professionals rely on it for performance metrics. Researchers use it to summarize experimental data. Even in everyday life, people calculate averages for budgeting, sports statistics, and personal tracking.
Using a reliable calculator ensures consistent and precise results every time.
Real-Life Applications of the Mean
The arithmetic mean is one of the most practical statistical tools used in daily life and professional environments.
Academic Performance
Teachers calculate average test scores to evaluate class performance. Students calculate their grade averages to track progress.
Business and Finance
Companies compute average revenue, average costs, and average profit margins to assess financial health.
Sports Statistics
Athletes are evaluated using average scores, batting averages, and performance metrics.
Science and Research
Scientists use the mean to summarize repeated measurements and experimental data.
Personal Budgeting
Individuals calculate average monthly expenses to plan their finances.
Because it condenses large amounts of data into one understandable number, the mean is one of the most essential statistical tools available.
Mean vs Median vs Mode
Many people confuse the mean with other measures of central tendency. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right measure for your data.
Mean
The arithmetic average of all numbers. Best used when data does not have extreme outliers.
Median
The middle value when numbers are arranged in order. Useful when data contains very large or very small values that could distort the mean.
Mode
The number that appears most frequently. Helpful for identifying common patterns in categorical or repeated data.
For example, consider the numbers: 5, 7, 8, 9, 100
The mean would be affected by 100 and become much higher.
The median would better represent the central trend.
Understanding when to use each measure improves data interpretation.
Handling Negative Numbers and Decimals
A reliable Mean Calculator must handle more than just simple whole numbers. Real datasets often include:
- Negative numbers
- Decimal values
- Large numbers
- Mixed positive and negative values
For example:
-5, 10, 15
(-5 + 10 + 15) = 20
20 ÷ 3 = 6.67
The calculator must correctly sum and divide values regardless of their sign or decimal precision. Proper rounding is also important to ensure the result remains mathematically accurate and consistent.
Common Mistakes When Calculating the Mean
Although the formula is simple, manual calculation mistakes are common.
- People sometimes forget to include all numbers in the sum.
- They may divide by the wrong total count.
- Errors can occur during addition.
- Rounding too early can change the final result.
- Some confuse the mean with the median.
Using a Mean Calculator eliminates these issues and ensures every input value is processed correctly.
When the Mean May Not Be the Best Choice
While the mean is powerful, it is not always the ideal measure of central tendency. If a dataset contains extreme outliers, the average can become misleading.
For example:
10, 12, 15, 18, 200
The number 200 significantly raises the mean and may not reflect the typical value in the dataset. In such situations, the median may provide a more accurate representation.
Understanding these limitations helps users interpret results correctly and apply statistics appropriately.
Frequently Asked Questions
It calculates the arithmetic average of a list of numbers by summing them and dividing by the total count.
Yes. In most cases, the term mean refers to the arithmetic average.
Yes. It processes both positive and negative values accurately.
Yes. Decimal inputs are calculated precisely.
You can enter as many numbers as your device allows, depending on input limits.
The mean will simply be that number.
Yes. It follows the standard arithmetic formula used worldwide.
Yes. It works efficiently for both small and large datasets.
Yes. It is completely free and requires no registration.
The mean is the average of all values, while the median is the middle value after sorting.
Some of our popular calculators: