Diamond Problem Solver
This Diamond Problem Solver helps you quickly find two integers that multiply to a given product and add to a given sum. Enter your values below to get instant answers with step-by-step explanations.
This calculator is designed for students, teachers, and anyone practicing algebra. It works with positive numbers, negative values, and zero, and clearly explains how the solution is found.
What Is a Diamond Problem in Math?
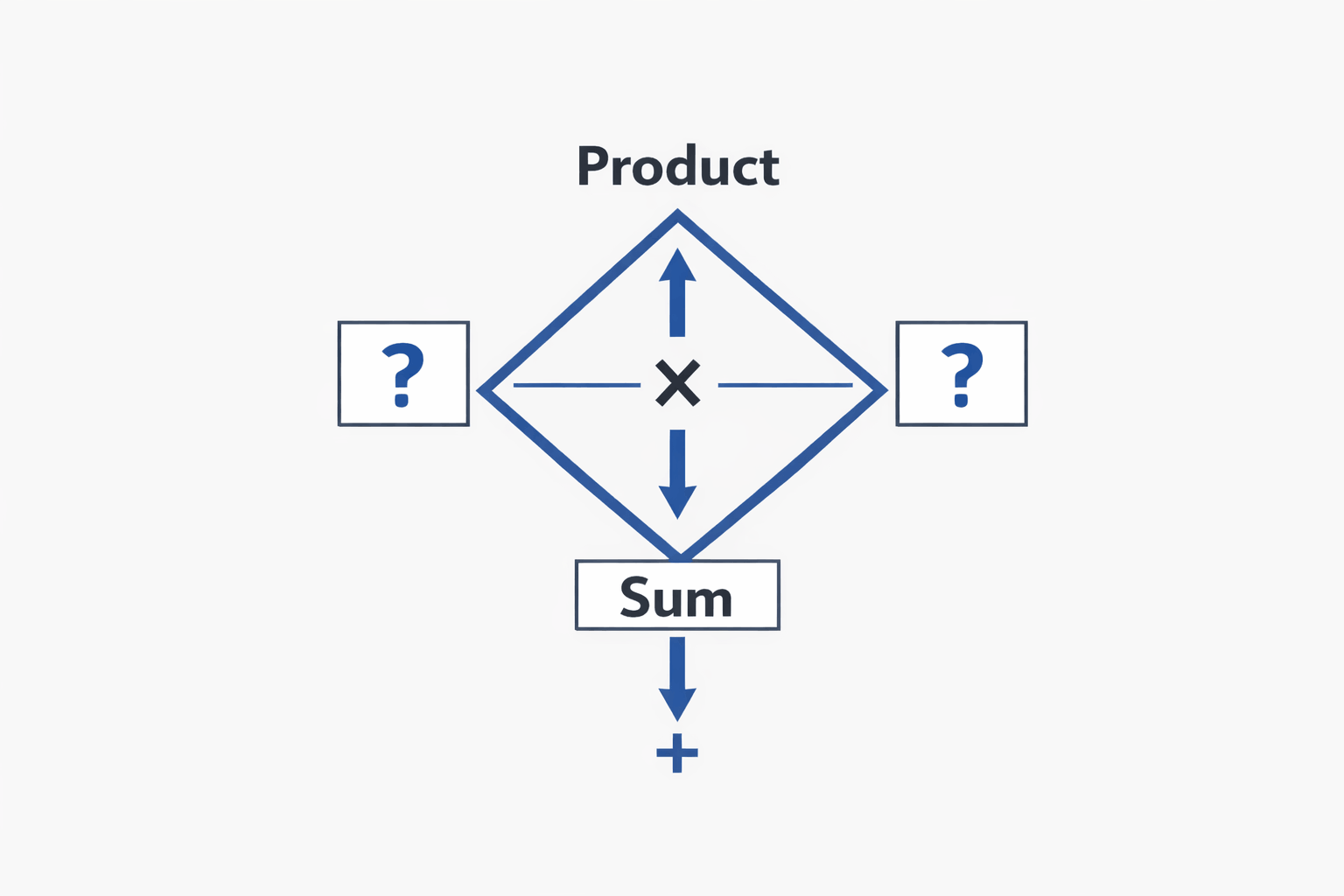
A diamond problem is a math exercise where you are given two numbers, a product and a sum, and your goal is to find two integers that satisfy both conditions at the same time. In other words, the two unknown numbers must multiply together to equal the product and add together to equal the sum.
These problems are commonly used in middle school and early algebra classes to build number sense and prepare students for factoring quadratic expressions. The diamond shape visually represents how multiplication and addition connect.
At the top of the diamond sits the product. At the bottom is the sum. The two side positions represent the numbers you must find. The challenge is identifying the pair that works for both operations.
Understanding this concept builds strong foundations in algebra, especially when moving toward polynomial factoring.
Table of Contents
How the Diamond Problem Solver Works
Our Diamond Problem Solver works by analyzing all possible factor pairs of the product. It then checks which pair adds up to the required sum.
Here is how the logic operates behind the scenes:
First, the calculator generates all integer factor pairs of the absolute value of the product. Next, it applies the correct sign combinations depending on whether the product and sum are positive or negative. Then it tests each pair to determine which one satisfies both the multiplication and addition conditions.
If a valid integer pair exists, it displays both numbers clearly along with verification. If no integer solution exists, the calculator correctly shows that no solution can be found.
This ensures mathematical accuracy while also helping users understand why a solution works.
Step-by-Step Example
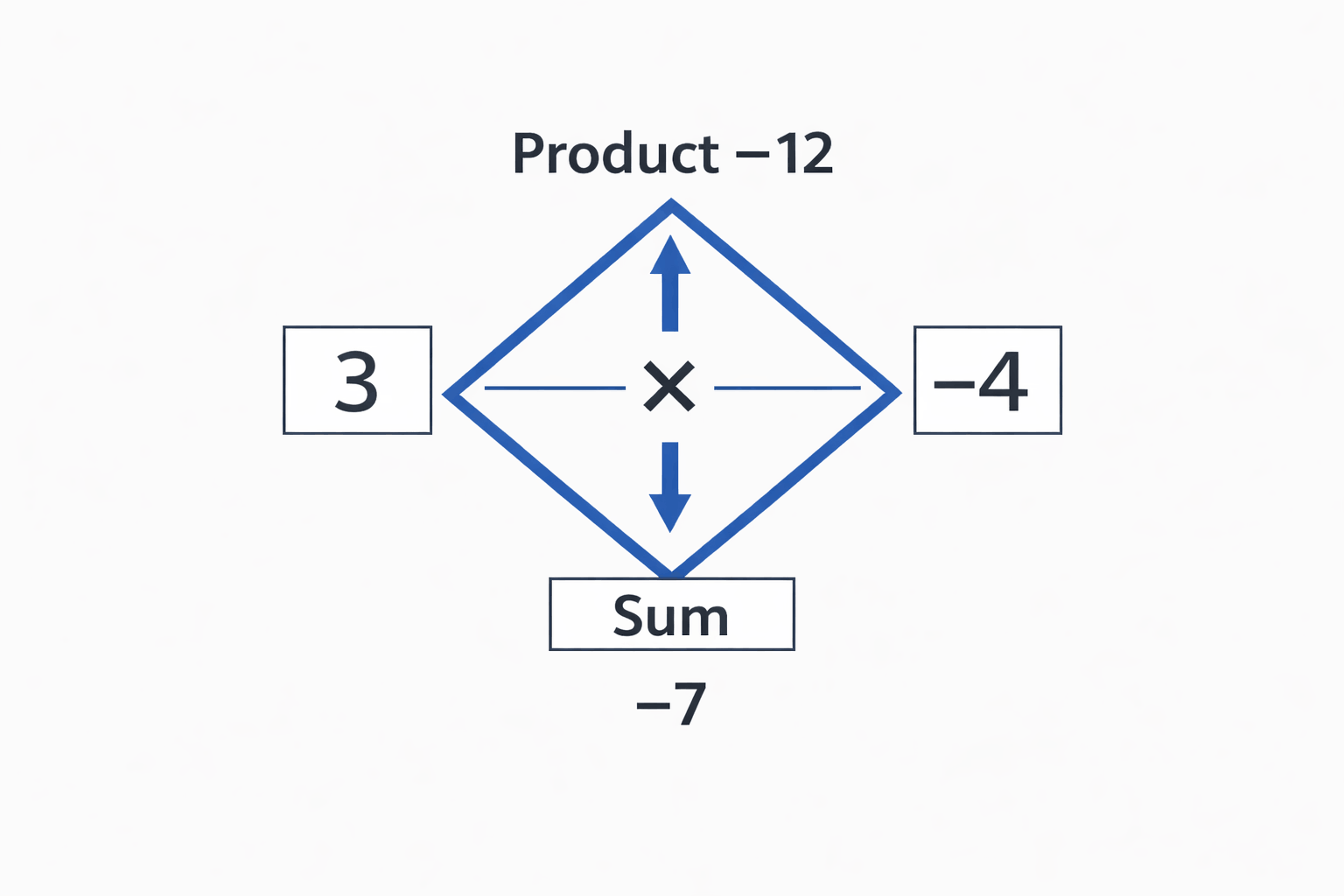
Example: Product = 36, Sum = -13
Step 1: List factor pairs of 36
1 and 36
2 and 18
3 and 12
4 and 9
6 and 6
Step 2:
Because the product is positive and the sum is negative, both numbers must be negative.
Step 3: Test negative pairs
-4 and -9
Step 4: Verify
-4 × -9 = 36
-4 + -9 = -13
Solution found. This method is exactly what the Diamond Problem Solver automates instantly.
Why This Tool Is Useful for Algebra
This type of number puzzle is more than just a practice exercise. It directly connects to factoring quadratic expressions.
For example:
x² + 14x + 45
To factor this expression, you must find two numbers that multiply to 45 and add to 14.
Using the Diamond Problem Solver, you enter:
Product = 45
Sum = 14
The result is 5 and 9.
This means the quadratic factors into:
(x + 5)(x + 9)
By practicing diamond problems, students become faster and more confident in algebraic factoring.
Handling Negative Numbers and Zero
A strong diamond solver must handle all sign combinations correctly.
• If the product is positive and the sum is positive, both numbers are positive.
• If the product is positive and the sum is negative, both numbers are negative.
• If the product is negative, one number is positive and the other is negative.
• If the product is zero, one number must be zero.
Many simple tools fail with negative numbers, but this calculator supports:
• Positive values
• Negative values
• Zero
• Cases with no integer solution
This ensures accurate results in all standard classroom scenarios.
Common Mistakes Students Make
Forgetting to consider negative factor pairs
When the product is positive and the sum is negative, both numbers must be negative. Many students only test positive factor pairs and miss the correct solution entirely. Always consider sign rules before testing combinations.
Only checking positive combinations
A product that is negative requires one positive and one negative number. Ignoring mixed sign pairs leads to incorrect answers. Sign logic is just as important as factor selection.
Mixing up product and sum
Some learners accidentally search for numbers that add to the product or multiply to the sum. The two conditions must be checked separately and carefully. One condition alone is not enough.
Ignoring zero cases
If the product is zero, one of the numbers must be zero. Students sometimes overlook this simple rule and begin testing unnecessary factor pairs. Zero cases are often the easiest to solve.
Stopping too early before testing all pairs
It is common to stop testing after checking only a few factor pairs. However, the correct solution might appear later in the list. Systematically checking all valid combinations ensures accuracy.
Why the Diamond Problem Solver Helps
The Diamond Problem Solver removes guesswork by automatically checking every valid factor pair using proper sign logic. It verifies both multiplication and addition conditions instantly, ensuring accurate and reliable results every time.
Random Mode and Learning Benefits
The random mode generates random solvable diamond problems so you can test your understanding repeatedly. Because it only generates problems that have integer solutions, it allows focused practice without frustration.
By using this tool consistently, students improve:
• Mental math skills
• Factor recognition speed
• Understanding of integer relationships
• Quadratic factoring confidence
Teachers can also use it during lessons to demonstrate number relationships in real time.
If you would like a deeper explanation with visual walkthrough examples, you can also watch this helpful YouTube video on solving diamond problems step by step
Frequently Asked Questions
Find clear, easy-to-understand answers to common questions about diamond problems, factor pairs, and how the calculation works.
What is a diamond problem in math?
A diamond problem is an exercise where you must find two integers that multiply to a given product and add to a given sum.
How do you solve a diamond problem?
You list all factor pairs of the product and check which pair adds to the required sum.
Can diamond problems include negative numbers?
Yes. Negative products and sums are valid, and correct sign logic must be applied.
What if no solution exists?
If no integer pair satisfies both conditions, then there is no integer solution.
Why is this used in algebra?
Diamond problems prepare students for factoring quadratic expressions.
What happens if the product is zero?
One of the numbers must be zero, and the other equals the sum.
Can the answers be the same number?
Yes. For example, product 36 and sum 12 gives 6 and 6.
Is this calculator free to use?
Yes. It provides instant results without login or registration.
Does it show steps?
Yes. The solver displays factor pairs and verification.
Is this suitable for middle school students?
Yes. It is designed for beginner to early algebra learners.
Some of our popular calculators: